Vaccine Distribution Supply Chain Prototype – UBC/MCG
The UBC CIC worked with faculty members in the Faculty of Applied Science at the University of British Columbia and start-up MCG to develop a prototype that demonstrates how distributors could review information from a dashboard and decide to take action if a vaccine batch begins to exceed its temperature requirement.
Overview
In collaboration, the UBC CIC worked with faculty and graduate students at UBC and start-up MCG to develop a prototype that could allow distributors to take action if a vaccine batch begins to exceed its temperature requirement, which would result in fewer losses. The solution also allows stakeholders to track the location of vaccine batches in near-real time.
Problem
During the long chain of distribution, from manufacturer to national storage facilities to regional storage facilities and finally to local clinics, vaccine batches are at risk of being spoiled before they reach their final destination. This results in losses for manufacturers and less availability of vaccines.
Approach
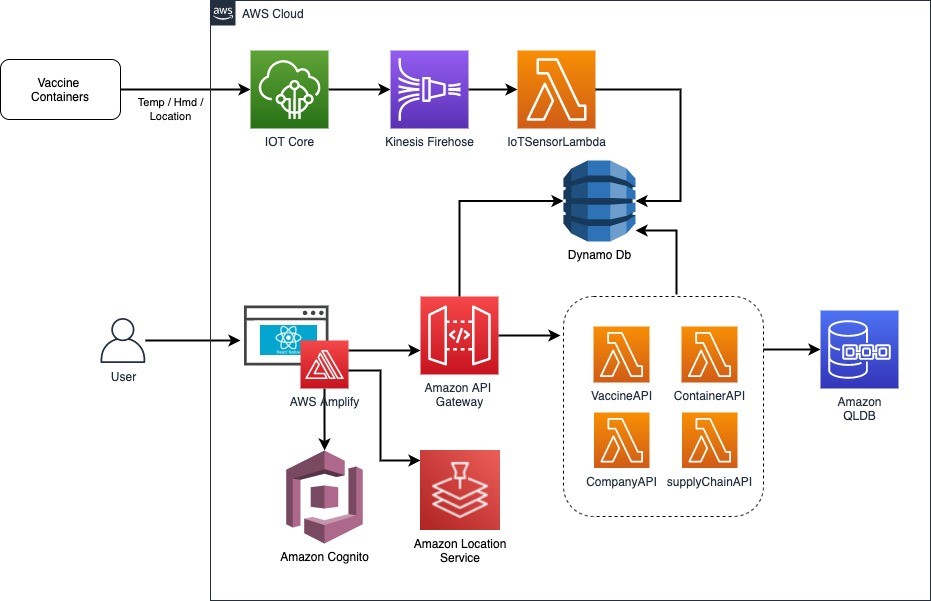
The prototype was developed in 2 phases. The first demonstrates the ability to monitor vaccines in transit. The UBC CIC developed a dashboard that could ingest GPS and temperature sensor data embedded in shipping containers to track the location and temperature of vaccine batches during transportation to ensure the integrity of the vaccine shipment. The prototype demonstrates how distributors could review information from a dashboard and decide to take action if a vaccine batch begins to exceed its temperature requirement. In a second phase, the prototype also demonstrates capabilities using the Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB) to create immutable and cryptographically verifiable records properties.
Link to Github repository: https://github.com/UBC-CIC/VaccineDistribution
Supporting artifacts
Architecture Diagram
Design artifacts
As part of the design process, a fictional Press Release and Frequently Asked Questions document are sometimes used as an important part of the design process.
FAQs
Here are some potential FAQs that could be asked if the solution is moved to production.
Customer FAQs
How does this solution minimize vaccine loss?
By monitoring conditions of the vaccine, using sensors, while it is in transport, distributors can take action quickly if an anomaly is detected, allowing them to minimize vaccine loss.
How do I use and access this solution?
The open source code for this prototype will be available on GitHub
What secure mechanisms this solution utilizes?
It leverages the AWS blockchain platform to maintain an immutable and cryptographically verifiable record of transactions of every movement a vaccine batch takes, based on QR codes or the unique identifiers (GS1 Standard).
Stakeholder FAQs
What is the infrastructure needed?
An AWS account. This is a cloud native solution
Is this scalable?
Yes. The entire solution is based on AWS managed components: AWS Lambda, Amazon QLDB, Amazon API Gateway, Amazon Cognito, Amazon S3, Amazon IoT Core, AWS Amplify.
Are there any planned upgrades to this solution?
This is an open source prototype. It is available to anyone to re-use or improve the code to make it production-ready.
Acknowledgements
The UBC CIC worked with the following professors, along with Montreal-based MCG to develop this prototype:
Dr. Zheng Liu – UBC Professor in the Faculty of Applied and Science School of Engineering
Dr. Zehua Wang – UBC Adjunct Professor in Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
About the University of British Columbia Cloud Innovation Centre (UBC CIC)
The UBC CIC is a public-private collaboration between UBC and Amazon Web Services (AWS). A CIC identifies digital transformation challenges, the problems or opportunities that matter to the community, and provides subject matter expertise and CIC leadership.
Using Amazon’s innovation methodology, dedicated UBC and AWS CIC staff work with students, staff and faculty, as well as community, government or not-for-profit organizations to define challenges, to engage with subject matter experts, to identify a solution, and to build a Proof of Concept (PoC). Through co-op and work-integrated learning, students also have an opportunity to learn new skills which they will later be able to apply in the workforce.